How to Encrypt Emails
Why Send Encrypted Emails?
In today's era of evolving privacy and security threats, taking basic steps to ensure the contents of your inbox are protected is critical. You may have heard that some people encrypt email, for example, as one way to keep their communication private. Encryption is a process of masking the contents of your email messages so that they cannot be read by unauthorized parties. Sensitive information like your social security number, password, login credentials and bank account numbers can otherwise be vulnerable to malicious intent when they are sent via email. For example identity thieves, hackers, and scammers are constantly finding new ways to trick to you into sharing these details to take advantage of you.
Whether using your inbox for personal or work, without the protection of secure encrypted email, your odds of experiencing a costly data breach may be higher. The statistics associated with data breaches are alarming. More than 13 billion data records have been lost or stolen in the last decade. Data breaches cost an average of $3.86 million in 2018 and have grown at an annual rate of 6.4% since 2017. It's not always easy to identify a data breach and they can take time to discover--sometimes as long as 197 days to find and another 69 days to contain. Email encryption is one preventative way to avoid becoming a cybersecurity victim.
What Does Encrypting an Email Do?
Today, close to 90% of emails both sent and received are encrypted. You might be wondering, what does encrypting an email do? Or what is making an encrypted email referring to? Encrypting an email is the process of essentially scrambling the data in the message to make it readable only to those who have the encryption keys. So if an unauthorized party intercepts your email somehow, the message itself will not be readable, keeping your information safe from exposure.
Encrypting your email is an excellent method of protecting yourself from the malicious threats lurking in your inbox, whether they be hackers, phishing scammers, spam senders, virus or other malware distributors. You can be protected from all of these groups if you have encrypted email, meaning that your personal or sensitive information will only be readable to those with the encryption keys and therefore harder to exploit.
In order to send encrypted email, there’s both easy and DIY ways to accomplish the task. For example, you can opt-in for an end-to-end encrypted email service or set up encryption protocol for your existing inbox. For the DIY approach, you’ll need the sender and the recipient to have matching setups. Some email services also offer built-in protocols for encryption.
How Email Encryption Works
When it comes to encrypting emails, you might wonder how it works. Encryption works at either the transport level or end-to-end.
With end-to-end encryption, your email is encrypted and decrypted only at the endpoints. At the final stage of being delivered, the email is decrypted for reading. End-to-end encryption is appealing for any messages you want to keep private from hackers and service providers alike.
Transport level encryption only helps keep your email protected while it's in the sending channel. When your message arrives at its destination, the email client decrypts it and stores it in plaintext for the recipient to read.
End-to-End Encryption
End-to-end encryption is increasingly popular in today's online world and an excellent option to consider to encrypt email. As a method of ensuring your email is safe at all stages of its communication, end-to-end encryption ensures an email can be read-only by the message sender and recipient, while remaining encrypted throughout the exchange process. Some encrypted email services offer the functionality built-in to their products.
For end-to-end email encryption to work, both the sender and the recipient must have a pair of cryptographic keys.
The process includes the following steps:
1. Both the email sender and recipient generate their public keys and exchange them with each other. Note that the private keys are kept only to themselves. When you sign up to use an encrypted email service you also receive a public key.
2. The message sender composes an email, encrypts it using the receiver’s public key, and sends it.
3. The message recipient receives an encrypted message, which they decrypt using their private key.
4. This way, the encryption and decryption happen on the user’s device. It prevents anyone in between, including the email service provider, from ever accessing the information that the email contains.
Transport-Level Encryption
Transport-level encryption is another very good option to encrypt email. Transport-level encryption means that an email is still composed and sent as plain text, but the moment it leaves your mailbox, it’s protected with a layer of encryption, like a suit of armor around your message. This method of encrypting email uses Transport Layer Security (TLS), or its predecessor Secure Sockets Layer (SSL) as cryptographic protocols encrypting the plain text messages only during server-to-server exchanges.
TLS was first developed by the Internet Engineering Task Force (IETF) in 1999 and is a popular internet security protocol engineered to ensure secure communications online, offering a good combination of privacy and data security.
When you send an email, your email client contacts the server to check whether it supports the requested protocol. The server shares a digital certificate confirming its identity. When it checks out, the two parties generate a unique exchange key used to encrypt and decrypt the messages. Whether you use TLS or end-to-end encryption, having some kind of protection in place to send email securely will reduce the chances of you becoming a victim.
An Email App with State-of-the-Art Encryption
Secure Encrypted Email Protocols
Sending secure email is possible with a few different protocols used for end-to-end encryption, including:
GNU Privacy Guard (GPG). GPG, also known as GnuPG, allows you to encrypt and sign your data and communications. As a free software replacement for Symantec’s PGP cryptographic standard, it features a robust key management system with access modules of many open public key directories. Easy integration with other applications like email is also a big plus.
Pretty Good Privacy (PGP). A popular algorithm used to encrypt and decrypt messages over email and add digital signatures to messages and files. It follows OpenPGP standard (RFC 4880) for PGP encryption. PGP involves a combination of hashing, data compression, and symmetric and asymmetric cryptography. PGP relies on a decentralized trust model and was developed to address security issues facing plain text messages. Within this model, there is more flexibility and control over how well you want your emails to be encrypted, but it requires a third-party encryption tool.
Secure/Multipurpose Internet Mail Extensions (S/MIME). A protocol for sending encrypted and digitally signed messages. For the receiver, this confirms that the message was not altered in transit. All of this only works if both parties have it set up on their email clients. S/MIME is built into most OSX and iOS devices and relies on a centralized authority to pick the encryption algorithm. S/MIME is used most often because it is built into large web-based email companies such as Apple and Outlook.
How to Send Encrypted Emails
Some very good news for all of us living in the era of technology innovation is that for anyone wondering how to encrypt email, the process is actually not too difficult to understand. There are a variety of easy to use options available for you to consider across email services like Gmail, Outlook, and Yahoo! as well as functionality to use on Apple devices, burner email services, password protected email and also file encryption products. Regardless of which option you decide is right for your situation, the important thing is to protect the privacy and security of your emails with encryption.
Gmail
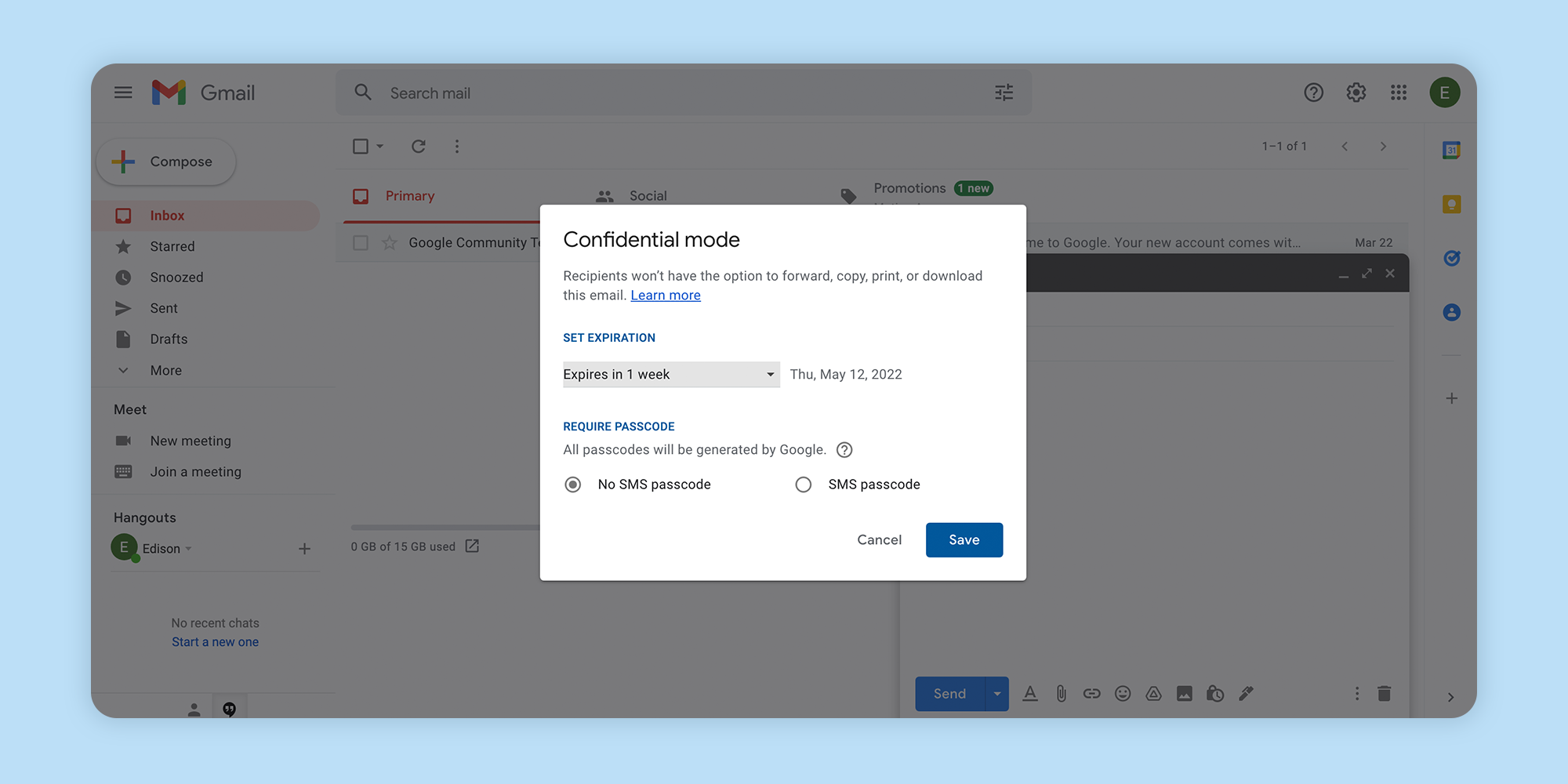
If you use Gmail, you can send emails and attachments in confidential mode to protect sensitive information. The feature allows you to set an expiration date for emails or revoke access at any time. Email recipients of a confidential message are unable to forward, copy, print, and download the email. However, while confidential mode helps prevent email recipients from sharing your message, it doesn't help if a recipient takes a photo or screenshot of your email information.
Google automatically encrypts all your emails in transit using Transport Layer Security (TLS), the standard means of performing a basic layer of encryption defense during transport. In addition to TLS, Gmail also supports S/MIME, an advanced encryption standard that encrypts actual message content. S/MIME is only available with G Suite Enterprise, G Suite for Education, and G Suite Enterprise for Education, and each sender and recipient must have it enabled for use.
To enable S/MIME, follow these steps:
1. Log in to your Google Admin console.
2. Go to Apps → G Suite → Gmail → User settings.
3. Select the domain or organization you want to configure.
4. Check the Enable S/MIME encryption for sending and receiving emails box.
5. Click Save.
Outlook
On its website Microsoft mentions that encryption is an important part of your file protection and information protection strategy. For your Microsoft 365 account, Outlook.com offers email encryption features to share confidential and personal information while ensuring that your email message stays encrypted. This is useful especially in the event that you don’t trust an email recipient’s email provider to be secure.
With Outlook, you can have multiple layers of encryption in place at the same time, with data at rest and in transit.
To send an encrypted email message in Outlook.com, follow these steps:
1. Log in to your Outlook.com account.
2. Click the blue New message button in the top-left corner.
3. Select the encryption option from the ribbon.
4. Click Encrypt or Encrypt & Prevent Forwarding (the latter makes it impossible for your message to be copied or forwarded).
5. Compose your message and click Send.
6. Outlook.com users can read encrypted email messages just like regular messages. The users of third-party mail services receive a message with instructions for how to read the encrypted message.
Yahoo
If your email account is with Yahoo, the service protects your messages in transit using TLS. However, because more encryption functionality is not available in the service you will need to use a free email encryption browser plugin to enable end-to-end encryption. Services like Mailvelope add missing encryption features to the user interface of common webmail providers, including Yahoo Mail, Gmail, and Outlook.com, among others.
To encrypt a Yahoo email message using Mailvelope, you can follow these steps:
1. Download Mailvelope for Google Chrome or Mozilla Firefox.
2. Configure Mailvelope to get started.
3. Open a new message in Yahoo Mail as usual.
4. Click the Mailvelope icon in the top-right corner.
5. Write your message and click Encrypt.
6. Send the encrypted message.
Worth noting is that the steps of encrypting email for Yahoo! with Mailvelope are nearly identical if you’re using other email providers like Gmail and Outlook.
Apple Devices
If you prefer to manage your email with Apple technology, you can rely on S/MIME support built-in as a default on your iOS device to help send email securely.
Follow these steps:
1. Go to advanced settings and switch S/MIME on.
2. Change “Encrypt by Default” to yes.
3. When you compose a message a lock icon will appear next to the recipient. Click the lock icon so it’s closed to encrypt the email.
4. Note: If the lock is blue, the email can be encrypted. If the lock is red, the recipient needs to turn on their S/MIME setting.
You can also send digitally signed and encrypted emails on a Mac. A digitally signed message lets email recipients verify your identity as the sender; an encrypted message offers an even higher level of security. To send signed messages, you must have a personal certificate in your keychain. To send encrypted messages, the recipient’s certificate must be in your keychain.
Do You Need a Burner Email?
Email encryption does have a limitation on its protection in the way that it only hides the contents of a message, not a sender’s actual email address. There is always a chance you will find yourself in a situation of needing to send an email anonymously to hide your identity. To do this, you might consider using a burner email or disposable mailbox service to access a temporary or “fake” email address.
There are three basic types of burner email services:
1. An alias that operates as an alternate form of the user’s actual email address. An email alias can be created with legacy email providers like Gmail or Yahoo! Mail. Email sent to an alias is filtered to a folder outside of the primary inbox. An alias address will still receive delivered email normally and may not be flagged in any way as a disposable address.
2. A forwarding account is created with a separate email domain. It forwards emails to the user’s primary account.
3. A non-forwarding or throwaway account is a one-time use email address. It does not forward emails and often becomes unavailable after a certain period of time. These are generally responsible for skewed bounce rates.
Burner email services include Guerrilla Mail and Zmail. With Guerilla Mail, you can set up a disposable email address and a password manager to manage multiple accounts. It is web-based with no registration required. Zmail allows you to email from a burner address and offers a desktop client.
Can You Send Encrypted Emails with a Password?
Passwords are likely the most common form of authentication we use for online security today. In fact, in 2021 the average person had as many as 100 passwords. Often, passwords are the only barrier between access to your personal information. If you’re concerned about the contents of a message and want extra peace of mind that only the intended email recipient will see it and nobody else, the ability to send password protected email seems like a wise choice.
As long as you can communicate the password to the recipient privately, your message can be read without the risk of anyone else seeing it first. A good password, should, first and foremost, be an original one. Try to avoid using repeat or easy to guess passwords. Don't use your own personal information in a password, like your name, birthday, or your pet's name, and try to avoid typical capitalizations like the first letter.
Sending an encrypted email with password protection is possible with certain email services, like Outlook.com for example. Ideally, the services you will use won't transfer any of your message (except for the subject line) to the recipient’s email server. This means that the message contents won’t even show up when searched for in a webmail or desktop client.
Is it Possible to Send Encrypted Files via Email?
Beyond encrypting the contents of your email message, another smart way to ensure the privacy of your information is to decide whether to encrypt documents for email. For example, if you send encrypted files via email attachments, you have more peace of mind that any sensitive information will not fall into the wrong hands if exposed to unauthorized recipients.
When sending a PDF file using Acrobat Reader or other versions, follow these simple steps to encrypt your file and send a secure email attachment:
1. Open the file in Acrobat Reader or other version
2. Choose “Tools” > “Protect.”
3. Select encrypt the file with a password.
4. Set password as desired. Click “OK” and then click “Save.”
5. Email the encrypted file.
6. Call or text the person receiving the encrypted file and give them the password. It will be case sensitive.
Conversely, if you're working with Excel or Word files (or any of Office suite), they also can be password protected:
1. Open the file within the Excel.
2. Choose “File” > “Info”.
3. Choose “Protect Workbook”
4. Select Encrypt with Password. The password is case sensitive and will be required every time the file is opened.
5. Set a password as desired. Click “OK” and then click “Save”.
Why Choose the Edison Mail App
Edison Mail is an app engineered with high standards of privacy and security. The app can help you have a secure and private email experience for all your accounts by ensuring all communication is encrypted during transport and delivery. Edison Mail is protected by one of the world’s most advanced security infrastructures. The app is safeguarded by multiple layers of security, including AES 256 encryption.
The average email user receives over 8,600 spy pixels (aka read receipts) from invasive advertisers attempting to track their behavior in their inbox every year. You can rely on Edison Mail's built-in anti-tracking technology to automatically block every single one of them, keeping your privacy intact. Since launching exclusively for iOS in 2016, Edison Mail has blocked over 1 billion spy pixels.
You can also protect your inbox with Face and Touch ID available on the Edison Mail iOS app.
Last, Edison Mail+ is a premium email subscription offering first-of-its-kind mobile security, including the ability to Verify Senders as authentic while getting alerts when suspicious emails enter your inbox. Verify Sender works quietly in the background, conducting four levels of deep-scanning to determine whether the email sender is legitimate or a scammer possibly attempting to cause you harm.